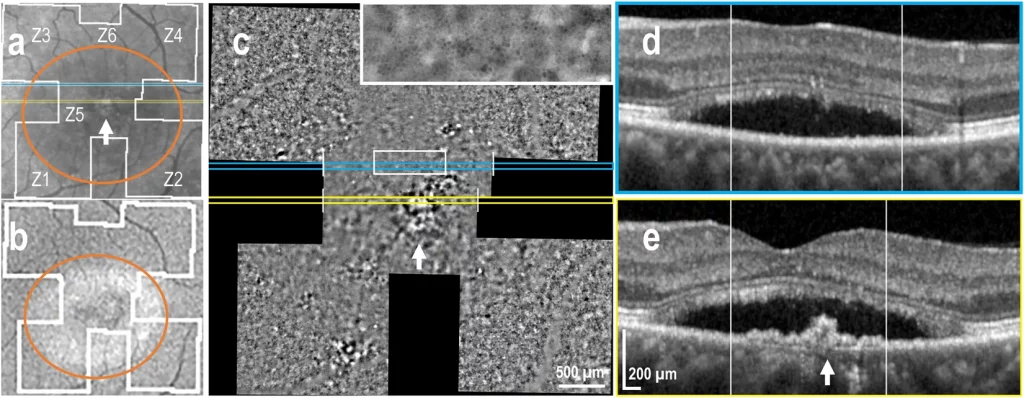
Andrea Cusumano, Francesco Martelli, Marco Lombardo, Fabian D’Apolito, Jacopo Sebastiani, Michele D’Ambrosio, Matteo Guelpa, Benedetto Falsini, Cellular analysis of retinal pigment epithelium and photoreceptors by transscleral optical imaging in inherited macular dystrophies. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science June 2024, Vol.65, 3409.
Mihaela Chitoroaga, Yoan Perez, Nicolas Owlya, Mickael Barbosa, Anna Chiara Nascimbeni, Yannic Pannatier-Schuetz, Daniela Gallo Castro, Aude Ambresin, Adaptive Optics-enhanced dual retinal layer imaging and region reflectivity-based segmentation: unveiling variances in healthy and diseased retina. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science June 2024, Vol.65, 3409.
Laura Kowalczuk, Sohrab Ferdowsi, christophe moser, Irmela Mantel, Francine F. Behar-Cohen, Morphological Analysis of Retinal Pigment Epithelium in Central Serous Chorioretinopathy using Adaptive Optics-Transscleral Flood Illumination. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science June 2024, Vol.65, 3392.
ARVO Imaging in the Eye Conference 2024, Christian Burri, Martin Zinkernagel, Chantal Dysli, In vivo assessment of human retinal pigment epithelium after selective retina therapy using transscleral flood illumination in combination with adaptive optics.
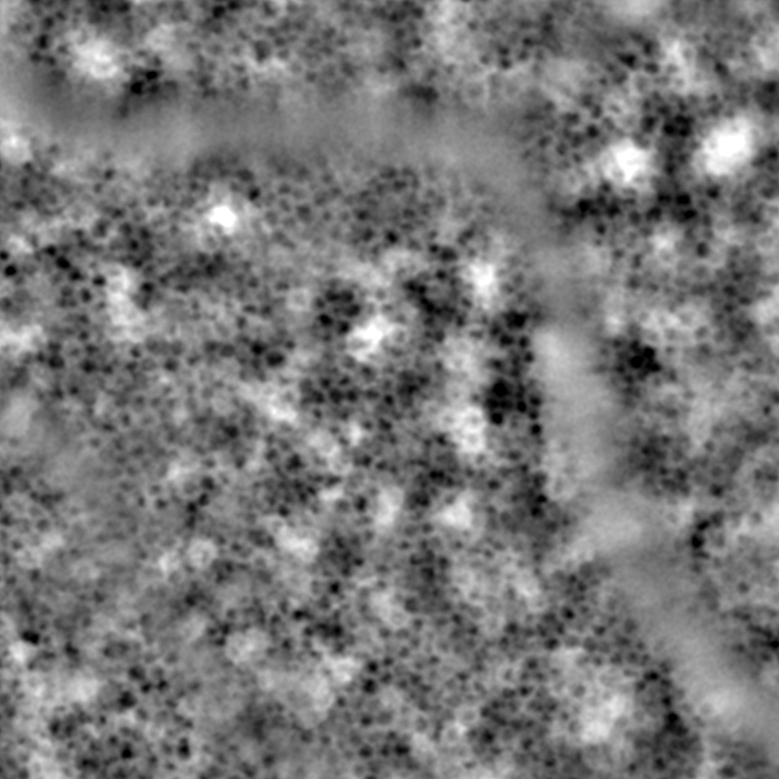
Leila Sara Eppenberger, Safa Mohanna, Michael A. Thiel and Martin K. Schmid, Exploring the Potential of in vivo Transscleral Optical Imaging by imaging of the retinal “3G” – Retinal Pigment Epithelium, Photoreceptors and Nerve Fiber Layers, Euretina 2022.
Safa Mohanna, Leila S. Eppenberger, Oliver Pfäffli, Lucas M. Bachmann, Michael A. Thiel, Martin K. Schmid Seeing Patterns – First Experiences of Transscleral Optical Imaging in Patients with Age-related Macular Degeneration, Euretina 2022.
Leila Sara Eppenberger, Safa Mohanna, Oliver Pfaeffli, Lucas M. Bachmann, Michael A. Thiel, Martin K. Schmid; First Clinic Experiences of Transscleral Optical Imaging to Study Retinal Pigment Epithelium and Photoreceptor Cells. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2022;63(7):4460 – F0139.
Sonja Simon-Zoula, Laura Kowalczuk, R dornier, Mathieu Kunzi, Antonio Iskandar, Zuzana Misutkova, Aurélia Gryczka, Aurélie Navarro, Fanny Jeunet, Irmela Mantel, Francine F Behar-Cohen, Timothé Laforest, Christophe Moser; Human retinal pigment epithelium cells can be imaged in vivo with a novel adaptive optics camera using transscleral illumination. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2022;63(7):1056 – F0303.
Irmela Mantel, Leonidas Solomos, Zuzana Misutkova, Antonio Iskandar, Aurélia Gryczka, Aurélie Navarro, Fanny Jeunet, Laura Kowalczuk, Rémy Dormier, Francine F Behar-Cohen, Christophe Moser; Transscleral optical imaging in non-neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2022;63(7):392 – F0430.
Vishal Govindahari, Laura Kowalczuk, Antonio Iskandar, Zuzana Misutkova, Aurélia Gryczka, Aurélie Navarro, Fanny Jeunet, Irmela Mantel, Christophe Moser, Francine F Behar-Cohen; Transscleral Optical Imaging (TOI) in Central Serous Chorioretinopathy – A novel imaging tool in retinal pigment epithelium visualization. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2022;63(7):1011 – F0258.
Antonio Iskandar, Irmela Mantel, Laura Kowalczuk, Aurelia Gryczka, Aurelie Navarro, Fanny Jeunet, Christophe Moser, Mathieu Kunzi, Francine F Behar-Cohen, Timothe Laforest; Transscleral optical phase imaging in non-neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021;62(8):1919.